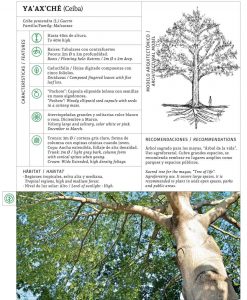
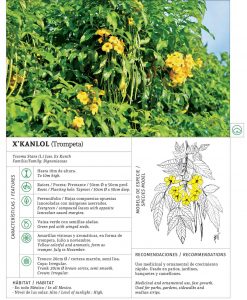
Plants
Knowledge of life and classification of living beings has reached such progress that is currently divided into five kingdoms or domains: Monera (which includes bacteria), Archaea (extremophiles), Protoctista (protozoa and algae), Fungi (fungus and yeasts), Animalia (animals metazoans) and Plantae (plants).
The kingdom or domain of the Plantae or plants are characterized by organisms with cells containing organelles, called chloroplasts with a photosensitive green pigment, chlorophyll and a metabolic system that allows them to produce their own organic matter and energy from the uptake of carbon dioxide, water and light.
With this they are able to produce energy, sugar molecules and release oxygen as a byproduct. They are therefore autotrophic organisms, because from these molecules changes can be made to use sugar as an energy source and thereby produce other compounds. That is why in ecology plants are defined as “primary producers”.
The first plants appeared about 416 million years ago during the Devonian; initially their shapes were similar to their ancestors the algae, and resulted in shapes similar to mosses; subsequently others appeared similar to ferns and then lead to the gymnosperms (such as conifers).

During the Cretaceous angiosperms or flowering plants appeared.
Throughout the whole chronology, plants have shown there an increasing complexity in their structures and likewise a lot has been extinct.
Plants have evolved into different forms of life: the great division is between the herbaceous and woody. Thus we have as life forms trees, shrubs, herbs, geophytes, rosettes, epiphytes, palm trees, climbers and parasitic plants.
The obvious component of biomes, of vegetation and landscapes, are plant communities with all visible forms of life that may harbor. Herbivores depend on plants and carnivores depend on herbivore populations. Finally, this whole chain also depends on human survival.
“Without the presence of plants we cannot conceive ecosystems and landscapes as they are today. Since plants are sessile, meaning they do not move; they form associations between them, communities and types of vegetation covering the continents in relation to different climates.”
Another important characteristic is that plants do not inhabit evenly on the planet and each species has its own distribution range.
So, there are widespread species and others of restricted distribution. Some are of more recent appearance and other are older. Some are relicts of acient large distributions.
Some regions of the world are of special interest, by its characteristic flora, and because they are ancient centers of origin for processes of plant domestication for different purposes such as food, textiles, ornamental, medicinal, etc.
A region, which for us is of special importance is Mesoamerica, which includes the southern part of Mexico. Of this, let us just remember that Mexico is the country that ranks fourth worldwide in biodiversity.
Here it is estimated to accommodate about 30 thousand species of plants (26495 species, data CONABIO) covering all possible forms of life.